-can increase from year to year only if ouput increases.
-adjusted for inflation
Nominal: value of output produced in current prices (CP x CQ)
-can increase from year to year if output or prices can increase.
-In the base year, the current prices will be equal to the constant price.
-Inyears after the base year, nominal GDP will exceed real GDP.
-In years before the base year, real GDP will exceed nominal GDP.
Price Index: measures inflation by tracking changes in the price of a market basket of goods compared with that in the base year.
Consumer Price index(CPI)
measures cost of a market basket of goods of a typical urban American Family
Price from year 2 - price from year 1
--------------------------------------------- X 100
Price from year 1
GDP Deflator
price index used to adjust from nominal to real GDP.
nominal GDP
----------------- X 100
real GDP
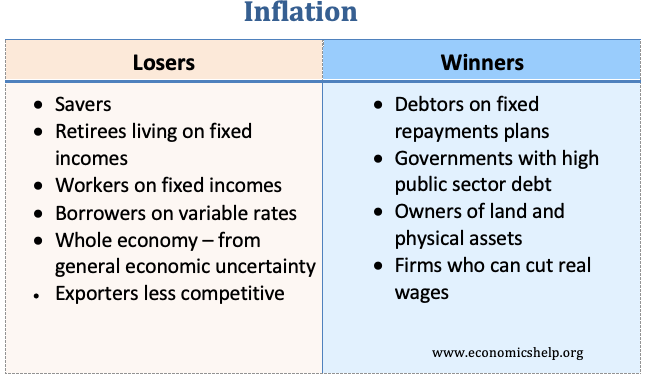
Inflation : general rise in price level
Deflation: general decline in price level
Disinflation: inflation rate itself declines
Real interest rate: cost of borrowing money thats adjusted for inflation.
Nominal interest rate: unajusted cost of borowing money
Demand pull inflation: "too many dollars facing too few goods" it is caused by excess of demand over output that pulls prices upward. It is triggered by an increase in aggregate demand which cause output & emplyment to rise which causes the price level to rise.
Cost push inflation: increase in factors of production
Ex: price of oil. lobor, steel.
increase in resource prices. output and emplyment will decline while price level is rising.
COLA = costs of living adjustment
wages have risen with inflation
Shoe leather costs= increased transaction cost of shopping around
menu costs= money it costs to change prices.
/what-is-balance-of-payments-components-and-deficit-3306278-Final1-c67946023d0f4cdcb7e7794de02947bc.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment