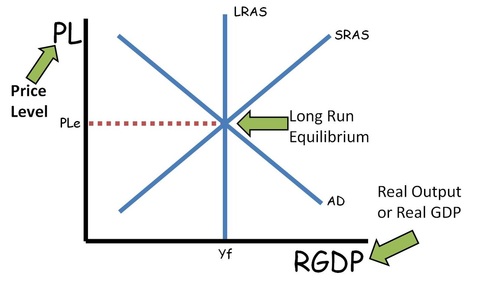
Full employment
- full employment equilibrium exists where AD intersects SRAS and LRAS at the same point
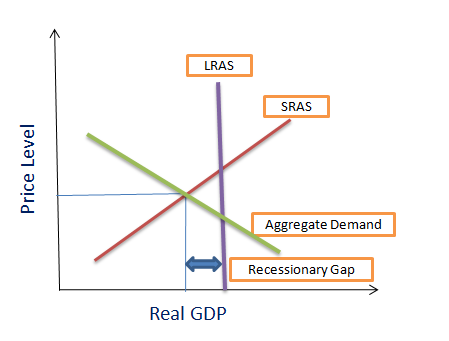
Recessionary Gap:
- a recession gap exists when equilibrium occurs below full employment output
Inflationary Gap:
-an inflationary gap occurs when equilibrium occurs beyond full employment output

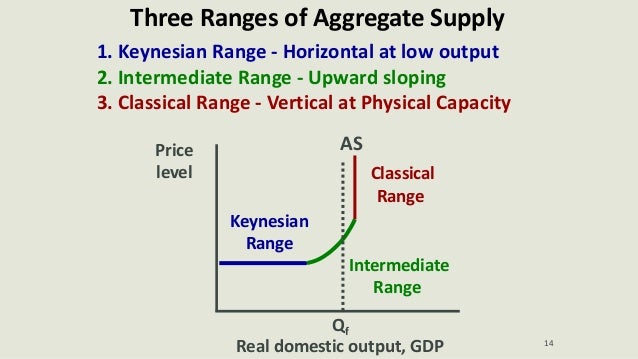
Keynesian Range :
-recession or depression
-not fully using all your resources
-below the FE
Intermediate :
-not fully using all your resources
-below the FE
Intermediate :
-Resources are getting closer to full employment levels which creates upward pressure on wages and prices
Classical or vertical range :
Classical or vertical range :
-When real GDP is at a level below the full employment level where any increase in demand will resolve only in an increase in prices.
Demand-Pull Inflation :
Demand-Pull Inflation :
-An increase in average price level resulting from an increase in total spending
in the economy.
-Total spending = C+Ig+G+Xn
nations AD
- increase in AD
in the economy.
-Total spending = C+Ig+G+Xn
nations AD
- increase in AD
Cost-Push Inflation :Occurs when firms respond to rising costs by increasing their prices to protect profit margins.
caused by
1. Rising unit labor costs
2. Increase in price of raw material/important components
3. Depreciation in exchange rate
causing a rise in import costs
4. An increase in business
taxes ex: VAT or environmental
taxes such as a carbon tax
1. Rising unit labor costs
2. Increase in price of raw material/important components
3. Depreciation in exchange rate
causing a rise in import costs
4. An increase in business
taxes ex: VAT or environmental
taxes such as a carbon tax
Factors Affecting Inflationary PressuresRise property prices > Increase consumer wealth > Demand-pull inflation risk
Increase world oil prices > Higher costs for businesses > Cost-push inflation risk
Depreciating exchange rate > Increased import prices + rising exports > Cost-push and Demand-pull risk
The rapid expansion of money and credit from banks > rising consumer spending financed by loans > Demand-pull inflation risk
Increase world oil prices > Higher costs for businesses > Cost-push inflation risk
Depreciating exchange rate > Increased import prices + rising exports > Cost-push and Demand-pull risk
The rapid expansion of money and credit from banks > rising consumer spending financed by loans > Demand-pull inflation risk
/what-is-balance-of-payments-components-and-deficit-3306278-Final1-c67946023d0f4cdcb7e7794de02947bc.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment